
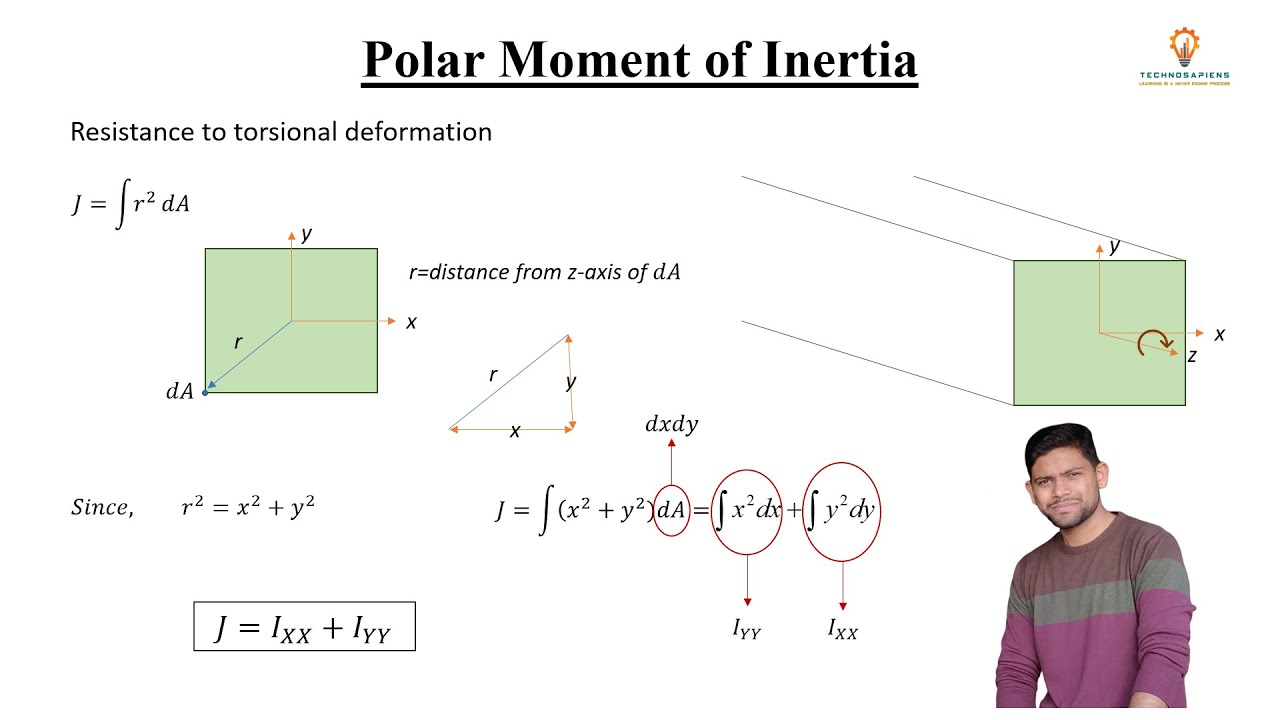
In the following sections, you can learn about the polar moment of inertia formulas for a hollow and a solid circle. For the latter, you'll need the polar moment. Do you need the resistance to bending of the tube with a bias cut on the end The SI units for moment of. Independently of the amount of transmitted power, it'll be mandatory to calculate the stresses and deformations in those shafts to avoid mechanical failure. It is not clear exactly what you are trying to do. Moment of inertia is the property of the body due to which it resists angular acceleration, which is the sum of the products of the mass of each particle in the body with the square of its distance from the axis of rotation. The area moment of inertia or second moment of area has a unit of dimension length 4, and should not be confused with the mass moment of inertia. Similarly, transmission shafts are used in power generation to send the energy from turbines to electric generators. The following is a list of area moments of inertia. The most common is the driveshaft in automobile drivetrains used to transmit power to the drive wheels. The area moment of inertia is a body’s characteristic that helps us exactly with this. Torsion-subjected members are widely present in engineering applications involving power transmission. The formula for the moment of inertia of a rectangular shape about an axis passing through its centroid and parallel to one of its sides is: I (1/12) x base x height3 For the rectangular shape in the center of the cross-section, the base is 100 mm and the height is 50 mm. The polar moment is essential for analyzing circular elements subjected to torsion (also known as shafts), while the area moment of inertia is for parts subjected to bending. Area Moment Of Inertia also known as the Second Moment of Area, is a geometrical property of an area which measures how its points are distributed about an. The polar moment of inertia and second moment of area are two of the most critical geometrical properties in beam analysis. The moment of inertia is also known as the Second Moment of the Area and is expressed mathematically as: Ix.
#Area moment of inertia how to#
If you're searching for how to calculate the polar moment of inertia (also known as the second polar moment of area) of a circular beam subjected to torsion, you're in the right place. This integral is called moment of inertia of an area or more fitting: The second moment of area, since the first moment ydA is multiplied by the moment arm. The reference axis is usually a centroidal axis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
